- Delhi, NCR
- +91-78400 59590
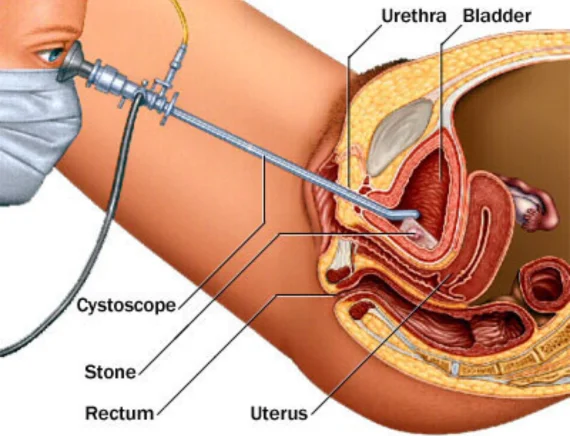
Urinary bladder stones, though not uncommon, often go unnoticed until they cause discomfort and complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of bladder stones, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Our focus will be on the insights provided by Dr. Prabhat Ranjan, a distinguished urologist renowned for his expertise in managing urinary disorders.
Symptoms of urinary bladder stones, also known as vesical or cystic stones, typically manifest as a combination of urinary tract irritation and obstruction signs. One of the primary symptoms is discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen, particularly when the bladder is full or during urination. This pain can vary from mild to severe and may feel like pressure, cramping, or sharp stabbing sensations. Additionally, individuals may experience frequent urges to urinate, often with only small amounts of urine being passed each time, a condition known as urinary urgency.
During urination, there may be difficulty initiating the stream or a weak urine flow, which can be accompanied by straining. Pain or burning sensations during urination, akin to those experienced with urinary tract infections, are also common. Hematuria, the presence of blood in the urine, may occur, giving the urine a pink, red, or brownish coloration.
Some individuals may notice changes in urinary habits, such as increased frequency of urination, nocturia (waking up at night to urinate), or urgency to urinate. In some cases, urinary retention can occur, where the bladder is unable to empty completely, leading to discomfort and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
As bladder stones can irritate the bladder lining and cause inflammation, other symptoms may include cloudy or foul-smelling urine due to the presence of infection or minerals from the stones. Chronic bladder irritation can also result in recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) or bladder pain syndrome, characterized by persistent pelvic discomfort.
If left untreated, bladder stones can lead to complications such as recurrent UTIs, urinary retention, bladder outlet obstruction, or even kidney damage. Therefore, prompt medical evaluation is essential if you experience any of these symptoms suggestive of bladder stones. Treatment options may include medications to manage pain and urinary symptoms, lifestyle modifications, dietary changes to prevent stone formation, or surgical procedures to remove the stones and alleviate bladder obstruction. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help prevent complications and improve overall urinary health.
With a specific focus on urological disorders, Dr. Prabhat Ranjan’s specialization ensures that patients receive tailored and effective treatments for conditions like ureteric stones.
Dr. Prabhat Ranjan’s expertise in urology sets him apart as a reliable source for addressing ureteric stones. With a focus on patient-centric care, he has dedicated his career to providing comprehensive solutions for urological issues.
From conservative management to surgical interventions, Dr. Ranjan outlines the array of treatment options available. Medications and lifestyle adjustments also feature prominently in his approach to alleviate the burden of kidney stones.
Prevention is often the best medicine. Hydration, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes form the cornerstone of Dr. Prabhat Ranjan’s preventive strategies, empowering individuals to take charge of their kidney health.

Copyright © 2024 Drprabhat . All rights reserved.